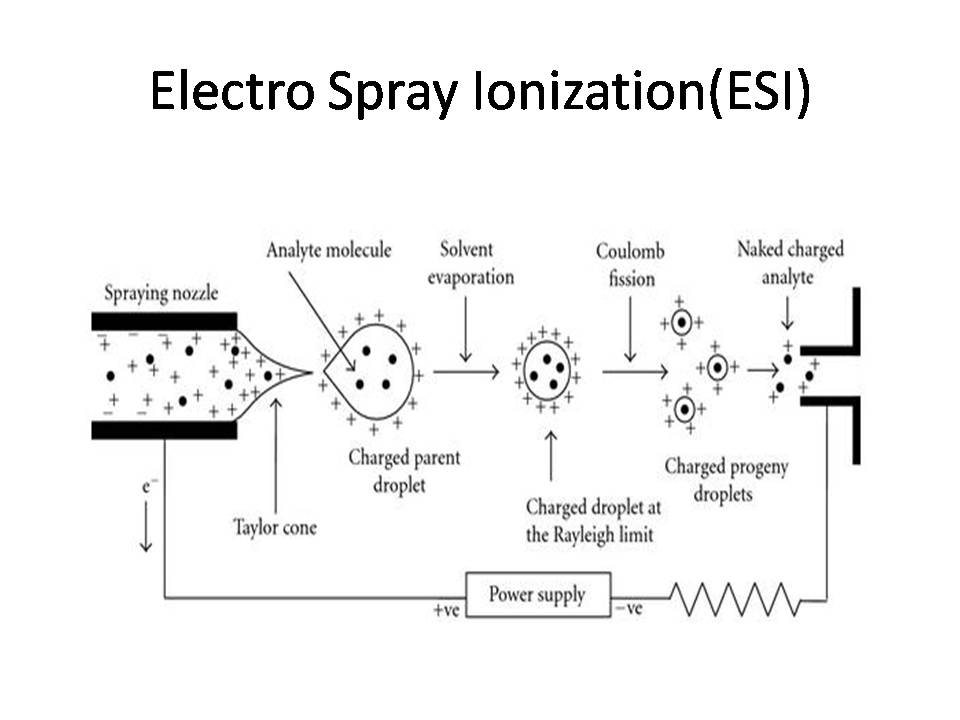
ESI– Electro Spray Ionization is most widely used ionization techniques in mass spectrometry.
Electrospray is a method of getting the solution phase ions into the gas phase so that they can be sampled in the Mass spectrometer.
Electro Spray Ionization is best suited for Ionic compounds with high polarity.
When an analyte is transferred from solution to the gas phase via ESI the analyte solution undergoes three major processes:
(a) Production of charged droplets
(b) Coulomb explosion and disintegration of the charged droplets
(c) Formation of gas-phase ions from the charged droplets
(a) Production of charged droplets:
·When the analyte solution is pumped through the high-voltage capillary – An electrochemical reaction of the solvent occurs, which causes an electron flow.
These accumulated charges (positive ions-which are formed by oxidation of solvent in positive ion mode) would be repelled by the high voltage capillary (of the same polarity) and then they would drift toward the liquid surface at the capillary outlet. However, the accumulated like charges at the surface are destabilized and finally the meniscus would be drawn out and deformed into a cone under the influence of a very high electric field (3-5 kV). This cone is called Taylor cone.
Taylor cone – The condition under which stable liquid cone can exist with competing forces of an electric field and the surface tension of the liquid.
This Taylor cone is the zone of high turbulence. At high field strength, it immediately starts ejecting a fine jet of liquid from its apex to form charged droplets.
.All these charged droplets are driven away from each other by coulombic repulsion and move along the direction of the electric fields.
· Under positive ion mode positively charged aerosol is formed and under negative ion mode negatively charged aerosol is formed.
(b) Coulomb explosion and disintegration of the charged droplets:
· The charges (say protons in positive ion mode) in the droplets are distributed on its surface with equidistant spacing to minimize the potential energy.
· There are two forces acting in the opposite direction in the charged droplets. One is the surface tension of charged droplets, which tries to retain the spherical shape of the droplet, and the other is the coulomb force of repulsion between the like charges on the surface, which tries to break the spherical shape of the charged droplet.
· When the solvent evaporation occurs, the size of droplet decreases until it reaches the point (Rayleigh limit)-where the surface tension can no longer sustain the coulomb force of repulsion and at this point “Coulomb explosion” or “coulomb fission” occurs. That is, the parent droplet disintegrates into smaller offspring droplets.
· The process of solvent evaporation and coulomb fission occurs repeatedly to generate smaller droplets.
(c) Formation of gas-phase ions from the charged droplets:
· As a series of solvent evaporation and coulomb fission, an extremely small charged droplets are formed which contains only one analyte molecule. Desolvation of this droplet causes its charges to land on the analyte molecules.
· Analyte enters the mass spectrometry-based on mass by charge (m/z)
Differences between ESI and APCI:
| Electro Spray Ionization (ESI) | Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization (APCI) |
| It is used for Natural substances, Biological macro molecules and Pharmaceuticals | Its primary application in the areas of ionization of low mass compounds |
| Highly polar compounds | Low and moderate polarity compounds |
| Ionic compounds | Compounds that do not ionize in solution (or) Highly fat soluble Compounds |
| It is used for least volatile (or) thermally unstable compounds | Not suitable for thermally unstable compounds |
| Ionization- Through protonated molecules or deprotonated molecules | Ionization- Through Ion- molecule reactions- Solvent molecules are ionized by corona discharge to generate stable reaction ions. Protons are transferred between these reaction ions and sample molecules either by adding or removing a proton. -it involves proton transfer reaction and electrophilic addition reaction. |